Linear Motor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A linear motor is an
A linear motor is an
 In this design, the force is produced by a moving linear
In this design, the force is produced by a moving linear
 In this design a large current is passed through a metal sabot across sliding contacts that are fed from two rails. The magnetic field this generates causes the metal to be projected along the rails.
In this design a large current is passed through a metal sabot across sliding contacts that are fed from two rails. The magnetic field this generates causes the metal to be projected along the rails.
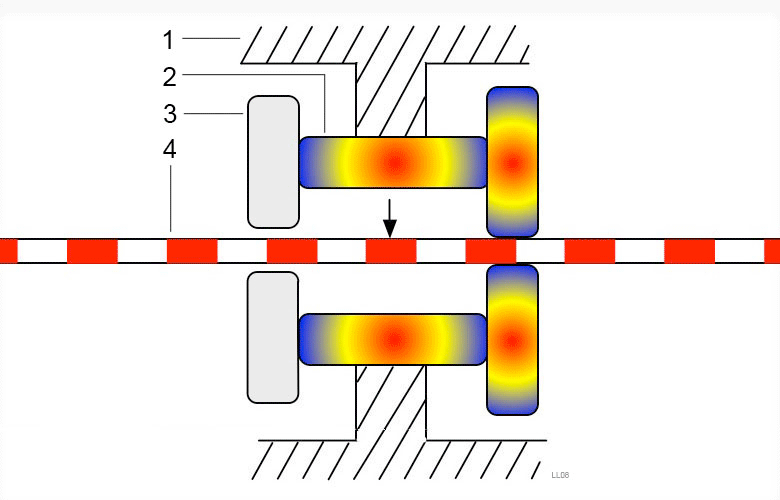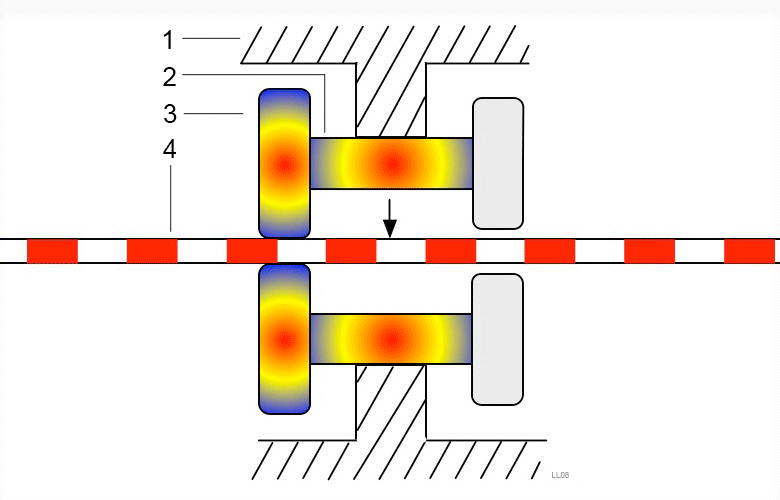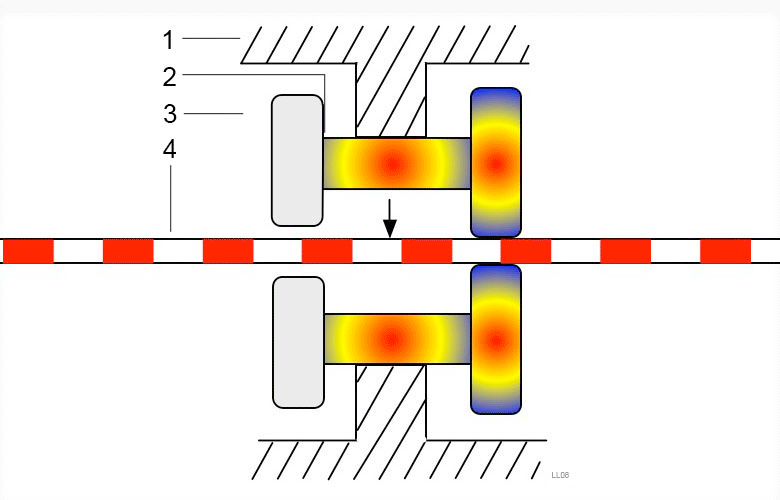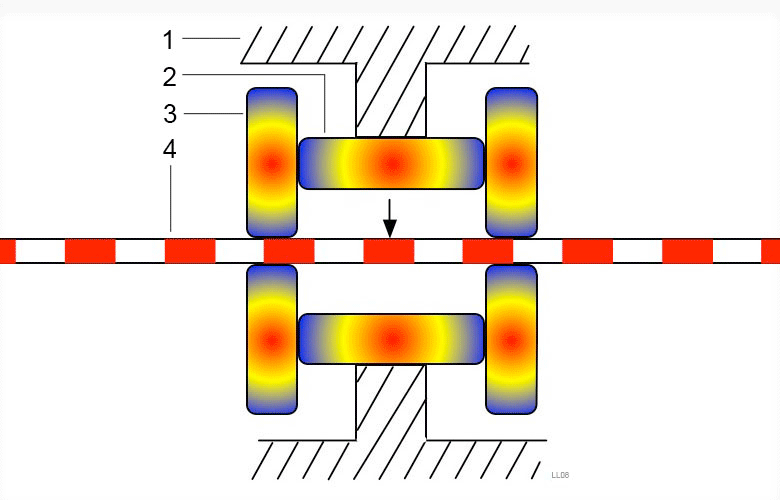 Piezoelectric drive is often used to drive small linear motors.
Piezoelectric drive is often used to drive small linear motors.

 Because of these properties, linear motors are often used in
Because of these properties, linear motors are often used in 
 * High-speed trains:
**
* High-speed trains:
**
Design equations, spreadsheet, and drawings
Motor torque calculation
{{DEFAULTSORT:Linear Motor Electric motors English inventions Linear motion
electric motor
An electric motor is an Electric machine, electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a Electromagneti ...
that has had its stator
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, sirens, mud motors or biological rotors. Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotating component of the system. In an electric mot ...
and rotor
Rotor may refer to:
Science and technology
Engineering
*Rotor (electric), the non-stationary part of an alternator or electric motor, operating with a stationary element so called the stator
* Helicopter rotor, the rotary wing(s) of a rotorcraft ...
"unrolled", thus, instead of producing a torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
(rotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
), it produces a linear force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a p ...
along its length. However, linear motors are not necessarily straight. Characteristically, a linear motor's active section has ends, whereas more conventional motors are arranged as a continuous loop.
A typical mode of operation is as a Lorentz
Lorentz is a name derived from the Roman surname, Laurentius, which means "from Laurentum". It is the German form of Laurence. Notable people with the name include:
Given name
* Lorentz Aspen (born 1978), Norwegian heavy metal pianist and keyboar ...
-type actuator, in which the applied force is linearly proportional to the current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
and the magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
.
Linear motors are by far most commonly found in high accuracy engineering applications. It is a thriving field of applied research with dedicated scientific conferences and engineering text books.
Many designs have been put forward for linear motors, falling into two major categories, low-acceleration and high-acceleration linear motors. Low-acceleration linear motors are suitable for maglev trains and other ground-based transportation applications. High-acceleration linear motors are normally rather short, and are designed to accelerate an object to a very high speed, for example see the coilgun
A coilgun, also known as a Gauss rifle, is a type of mass driver consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almos ...
.
High-acceleration linear motors are typically used in studies of hypervelocity
Hypervelocity is very high velocity, approximately over 3,000 meters per second (6,700 mph, 11,000 km/h, 10,000 ft/s, or Mach 8.8). In particular, hypervelocity is velocity so high that the strength of materials upon impact is v ...
collisions, as weapon
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, s ...
s, or as mass driver
A mass driver or electromagnetic catapult is a proposed method of non-rocket spacelaunch which would use a linear motor to accelerate and catapult payloads up to high speeds. Existing and contemplated mass drivers use coils of wire energized by e ...
s for spacecraft propulsion
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric e ...
. They are usually of the AC linear induction motor
A linear induction motor (LIM) is an alternating current (AC), asynchronous linear motor that works by the same general principles as other induction motors but is typically designed to directly produce motion in a straight line. Characteristic ...
(LIM) design with an active three-phase
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ) is a common type of alternating current used in electricity generation, Electric power transmission, transmission, and Electric power distribution, distribution. It is a type of polyphase system empl ...
winding on one side of the air-gap and a passive conductor plate on the other side. However, the direct current homopolar linear motor railgun
A railgun or rail gun is a linear motor device, typically designed as a weapon, that uses Electromagnet, electromagnetic force to launch high velocity projectiles. The projectile normally does not contain explosives, instead relying on the proj ...
is another high acceleration linear motor design. The low-acceleration, high speed and high power motors are usually of the linear synchronous motor (LSM) design, with an active winding on one side of the air-gap and an array of alternate-pole magnets on the other side. These magnets can be permanent magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, ...
s or electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the ...
s. The motor for the Shanghai maglev train, for instance, is an LSM.
Types
Brushless
Brushless linear motors are members of the Synchronous motor family. They are typically used in standardlinear stage
A linear stage or translation stage is a component of a precise motion system used to restrict an object to a single axis of motion. The term linear slide is often used interchangeably with "linear stage", though technically "linear slide" refe ...
s or integrated into custom, high performance positioning systems
A high performance positioning system (HPPS) is a type of positioning system consisting of a piece of electromechanics equipment (e.g. an assembly of linear stages and rotary stages) that is capable of moving an object in a three-dimensional space ...
. Invented in late 1980s by Anwar Chitayat at Anorad Corporation, now Rockwell Automation
Rockwell Automation, Inc. is an American provider of industrial automation whose brands include Allen-Bradley, FactoryTalk software and LifecycleIQ Services.
Headquartered in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, Rockwell Automation employs approximately 26,000 ...
, and helped improving throughput and quality of industrial manufacturing processes.
Brush
Brush (electric)
A brush or carbon brush is an electrical contact which conducts current between stationary wires and moving parts, most commonly in a rotating shaft. Typical applications include electric motors, alternators and electric generators. The lifespan ...
linear motors were used in industrial automation applications prior to the invention of Brushless linear motors. Compared with three phase
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ) is a common type of alternating current used in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system employing three wires (or four including an optional neutral ...
Brushless motors, which are typically being used today, brush motors operates with a single phase. Brush linear motors have lower cost since they do not need moving cables and three phase servo drives. However, they require higher maintenance since their brushes wear out.
Synchronous
In this design the rate of movement of the magnetic field is controlled, usually electronically, to track the motion of the rotor. For cost reasons synchronous linear motors rarely use commutators, so the rotor often contains permanent magnets, orsoft iron
A magnetic core is a piece of magnetic material with a high magnetic permeability used to confine and guide magnetic fields in electrical, electromechanical and magnetic devices such as electromagnets, transformers, electric motors, generators, in ...
. Examples include coilgun
A coilgun, also known as a Gauss rifle, is a type of mass driver consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almos ...
s and the motors used on some maglev
Maglev (derived from '' magnetic levitation''), is a system of train transportation that uses two sets of electromagnets: one set to repel and push the train up off the track, and another set to move the elevated train ahead, taking advantage ...
systems, as well as many other linear motors. In high precision industrial automation linear motors are typically configured with a magnet stator and a moving coil. A Hall effect sensor
A Hall effect sensor (or simply Hall sensor) is a type of sensor which detects the presence and magnitude of a magnetic field using the Hall effect. The output voltage of a Hall sensor is directly proportional to the strength of the field. ...
is attached to the rotor to track the magnetic flux
In physics, specifically electromagnetism, the magnetic flux through a surface is the surface integral of the normal component of the magnetic field B over that surface. It is usually denoted or . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber ( ...
of the stator. The electrical current is typically provided from a stationary servo drive
A servo drive is an electronic amplifier used to power electric servomechanisms.
A servo drive monitors the feedback signal from the servomechanism and continually adjusts for deviation from expected behavior.
Function
A servo drive receives a c ...
to the moving coil by a moving cable inside a cable carrier
Cable carriers, also known as drag chains, energy chains, or cable chains depending on the manufacturer, are guides designed to surround and guide flexible electrical cables and hydraulic or pneumatic hoses connected to moving automated machin ...
.
Induction
 In this design, the force is produced by a moving linear
In this design, the force is produced by a moving linear magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
acting on conductors in the field. Any conductor, be it a loop, a coil or simply a piece of plate metal, that is placed in this field will have eddy current
Eddy currents (also called Foucault's currents) are loops of electrical current induced within conductors by a changing magnetic field in the conductor according to Faraday's law of induction or by the relative motion of a conductor in a mag ...
s induced in it thus creating an opposing magnetic field, in accordance with Lenz's law
Lenz's law states that the direction of the electric current induced in a conductor by a changing magnetic field is such that the magnetic field created by the induced current opposes changes in the initial magnetic field. It is named after p ...
. The two opposing fields will repel each other, thus creating motion as the magnetic field sweeps through the metal.
Homopolar
Tubular
Efficient and compact design applicable to replacement ofpneumatic cylinder
Pneumatic cylinders (sometimes known as air cylinders) are mechanical devices which use the power of compressed gas to produce a force in a reciprocating linear motion.
Like hydraulic cylinders, something forces a piston to move in the desire ...
s.
Piezo electric
 Piezoelectric drive is often used to drive small linear motors.
Piezoelectric drive is often used to drive small linear motors.
History

Low acceleration
The history of linear electric motors can be traced back at least as far as the 1840s, to the work ofCharles Wheatstone
Sir Charles Wheatstone FRS FRSE DCL LLD (6 February 1802 – 19 October 1875), was an English scientist and inventor of many scientific breakthroughs of the Victorian era, including the English concertina, the stereoscope (a device for di ...
at King's College London
King's College London (informally King's or KCL) is a public research university located in London, England. King's was established by royal charter in 1829 under the patronage of King George IV and the Duke of Wellington. In 1836, King's ...
, but Wheatstone's model was too inefficient to be practical. A feasible linear induction motor is described in the (1905 - inventor Alfred Zehden of Frankfurt-am-Main), for driving trains or lifts. The German engineer Hermann Kemper
Hermann Kemper (5 April 1892 in Nortrup – 13 July 1977) was a German engineer and pioneer in magnetic levitation.
Herman Kemper began his research on magnetic levitation in 1922. In 1933, Kemper constructed a working circuit for hovering on ...
built a working model in 1935. In the late 1940s, Dr. Eric Laithwaite
Eric Roberts Laithwaite (14 June 1921 – 27 November 1997) was a British electrical engineer, known as the "Father of Maglev" for his development of the linear induction motor and maglev rail system.
Biography
Eric Roberts Laithwaite wa ...
of Manchester University
, mottoeng = Knowledge, Wisdom, Humanity
, established = 2004 – University of Manchester Predecessor institutions: 1956 – UMIST (as university college; university 1994) 1904 – Victoria University of Manchester 1880 – Victoria Univer ...
, later Professor of Heavy Electrical Engineering at Imperial College
Imperial College London (legally Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine) is a public research university in London, United Kingdom. Its history began with Prince Albert, consort of Queen Victoria, who developed his vision for a cu ...
in London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
developed the first full-size working model. In a single sided version the magnetic repulsion forces the conductor away from the stator, levitating it, and carrying it along in the direction of the moving magnetic field. He called the later versions of it magnetic river Magnetic river is an electrodynamic magnetic levitation (maglev) system designed by Fredrick Eastham and Eric Laithwaite in 1974. It consists of a thin conductive plate on an AC linear induction motor. Due to the transverse flux and the geometry, ...
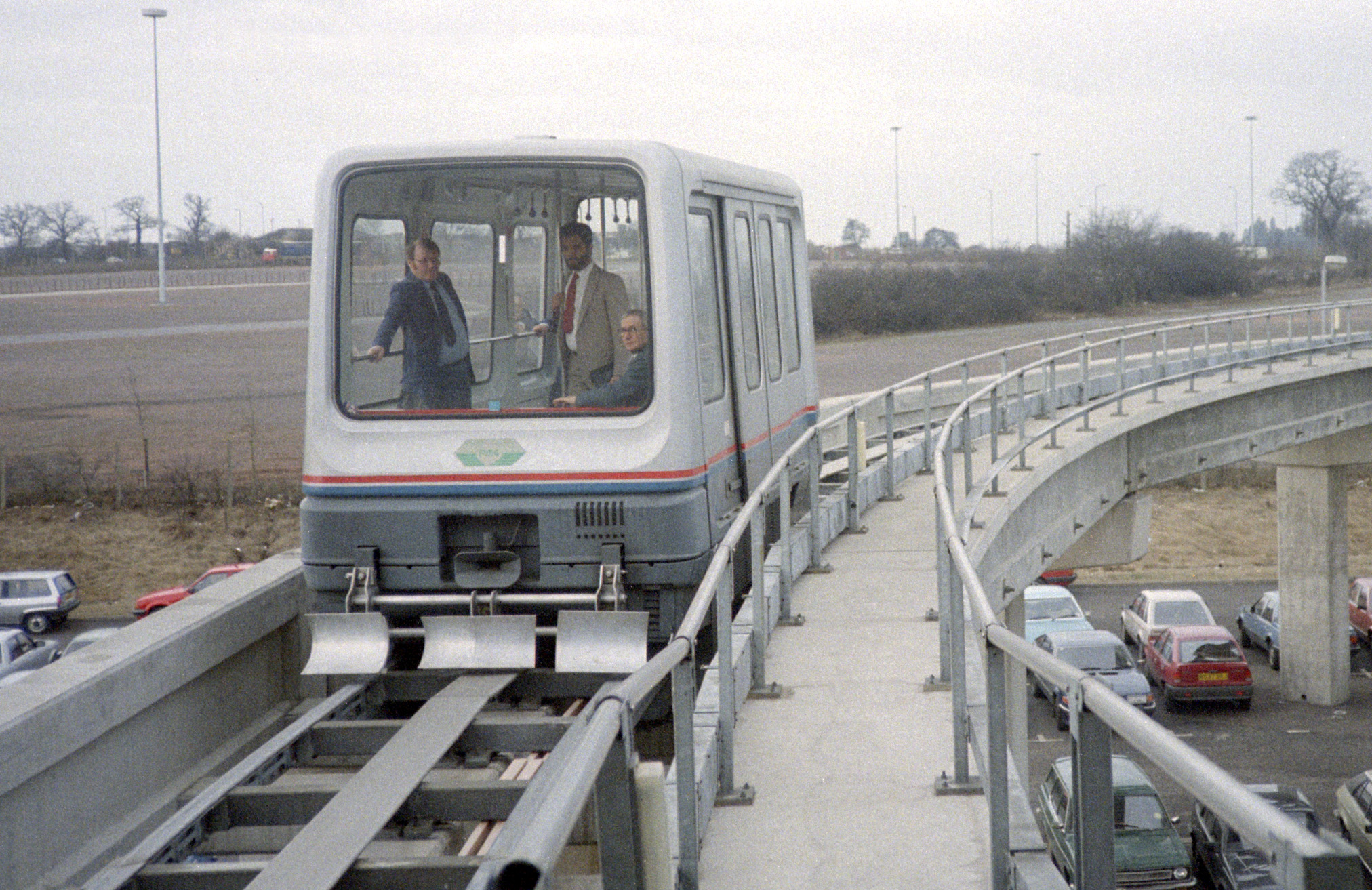
. The technologies would later be applied, in the 1984, Air-Rail Link
The Air-Rail Link is a people mover linking Birmingham Airport with Birmingham International railway station and the National Exhibition Centre in England. The current system, originally known as SkyRail, replaced the earlier Birmingham Maglev ...
shuttle, between Birmingham's airport and an adjacent train station.
 Because of these properties, linear motors are often used in
Because of these properties, linear motors are often used in maglev
Maglev (derived from '' magnetic levitation''), is a system of train transportation that uses two sets of electromagnets: one set to repel and push the train up off the track, and another set to move the elevated train ahead, taking advantage ...
propulsion, as in the Japanese Linimo magnetic levitation train line near Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a population of 2.3million in 2020. Located on the Pacific coast in central Honshu, it is the capital and the most pop ...
. However, linear motors have been used independently of magnetic levitation, as in the Bombardier Innovia Metro
Innovia Metro is an automated rapid transit system manufactured by Alstom. Innovia Metro systems run on conventional metal rails and pull power from a third rail, but are powered by a linear induction motor that provides traction by pulling on ...
systems worldwide and a number of modern Japanese subways, including Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 ...
's Toei Ōedo Line
The is a subway line in Tokyo, Japan, operated by the Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation (Toei). It commenced full operations on December 12, 2000; using the Japanese calendar this reads "12/12/12" as the year 2000 equals Heisei 12. T ...
.
Similar technology is also used in some roller coaster
A roller coaster, or rollercoaster, is a type of amusement ride that employs a form of elevated railroad track designed with tight turns, steep slopes, and sometimes inversions. Passengers ride along the track in open cars, and the rides are o ...
s with modifications but, at present, is still impractical on street running tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
s, although this, in theory, could be done by burying it in a slotted conduit.
Outside of public transportation, vertical linear motors have been proposed as lifting mechanisms in deep mine
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to:
Extraction or digging
* Miner, a person engaged in mining or digging
*Mining, extraction of mineral resources from the ground through a mine
Grammar
*Mine, a first-person English possessive pronoun
...
s, and the use of linear motors is growing in motion control
Motion control is a sub-field of automation, encompassing the systems or sub-systems involved in moving parts of machines in a controlled manner. Motion control systems are extensively used in a variety of fields for automation purposes, includi ...
applications. They are also often used on sliding doors, such as those of low floor
Accessibility is the design of products, devices, services, vehicles, or environments so as to be usable by people with disabilities. The concept of accessible design and practice of accessible development ensures both "direct access" (i. ...
trams such as the Alstom Citadis
The Alstom Citadis is a family of low-floor trams and light rail vehicles built by Alstom. , over 2,300 Citadis trams have been sold and 1,800 tramways are in revenue service throughout the world, with operations in all six inhabited continents ...
and the Socimi Eurotram
The Socimi Eurotram (later sold as the Bombardier Flexity Outlook (E)) was an electric tramcar designed for the tram system of Compagnie de Transports Strasbourgeois (CTS). Initially produced by Socimi, after the company became bankrupt Eurotrams ...
. Dual axis linear motors also exist. These specialized devices have been used to provide direct ''X''-''Y'' motion for precision laser cutting of cloth and sheet metal, automated drafting, and cable forming. Most linear motors in use are LIM (linear induction motor), or LSM (linear synchronous motor). Linear DC motors are not used due to higher cost and linear SRM suffers from poor thrust. So for long run in traction LIM is mostly preferred and for short run LSM is mostly preferred.

High acceleration
High-acceleration linear motors have been suggested for a number of uses. They have been considered for use asweapon
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, s ...
s, since current armour-piercing
Armour-piercing ammunition (AP) is a type of projectile designed to penetrate either body armour or vehicle armour.
From the 1860s to 1950s, a major application of armour-piercing projectiles was to defeat the thick armour carried on many warsh ...
ammunition tends to consist of small rounds with very high kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its accele ...
, for which just such motors are suitable. Many amusement park launched roller coaster
The launched roller coaster is a modern form of roller coaster. A launched coaster initiates a ride with high amounts of acceleration via one or a series of linear induction motors (LIM), linear synchronous motors (LSM), catapults, tires, chains ...
s now use linear induction motors to propel the train at a high speed, as an alternative to using a lift hill
A lift hill, or chain hill, is an upward-sloping section of track on a roller coaster on which the roller coaster train is mechanically lifted to an elevated point or peak in the track. Upon reaching the peak, the train is then propelled from th ...
. The United States Navy is also using linear induction motors in the Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System
The Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS) is a type of aircraft launching system developed by General Atomics for the United States Navy. The system launches carrier-based aircraft by means of a catapult employing a linear induction ...
that will replace traditional steam catapult
An aircraft catapult is a device used to allow aircraft to take off from a very limited amount of space, such as the deck of a vessel, but can also be installed on land-based runways in rare cases. It is now most commonly used on aircraft carrier ...
s on future aircraft carriers. They have also been suggested for use in spacecraft propulsion
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric e ...
. In this context they are usually called mass driver
A mass driver or electromagnetic catapult is a proposed method of non-rocket spacelaunch which would use a linear motor to accelerate and catapult payloads up to high speeds. Existing and contemplated mass drivers use coils of wire energized by e ...
s. The simplest way to use mass drivers for spacecraft propulsion would be to build a large mass driver that can accelerate cargo up to escape velocity
In celestial mechanics, escape velocity or escape speed is the minimum speed needed for a free, non- propelled object to escape from the gravitational influence of a primary body, thus reaching an infinite distance from it. It is typically ...
, though RLV launch assist like StarTram
StarTram is a proposed space launch system propelled by maglev. The initial Generation 1 facility would launch cargo only, launching from a mountain peak at an altitude of with an evacuated tube staying at local surface level; it has been clai ...
to low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never mor ...
has also been investigated.
High-acceleration linear motors are difficult to design for a number of reasons. They require large amounts of energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
in very short periods of time. One rocket launcher design calls for 300 GJ for each launch in the space of less than a second. Normal electrical generator
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power (mechanical energy) or fuel-based power (chemical energy) into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas ...
s are not designed for this kind of load, but short-term electrical energy storage methods can be used. Capacitors are bulky and expensive but can supply large amounts of energy quickly. Homopolar generator
A homopolar generator is a DC electrical generator comprising an electrically conductive disc or cylinder rotating in a plane perpendicular to a uniform static magnetic field. A potential difference is created between the center of the disc and th ...
s can be used to convert the kinetic energy of a flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, ass ...
into electric energy very rapidly. High-acceleration linear motors also require very strong magnetic fields; in fact, the magnetic fields are often too strong to permit the use of superconductors
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike ...
. However, with careful design, this need not be a major problem.
Two different basic designs have been invented for high-acceleration linear motors: railgun
A railgun or rail gun is a linear motor device, typically designed as a weapon, that uses Electromagnet, electromagnetic force to launch high velocity projectiles. The projectile normally does not contain explosives, instead relying on the proj ...
s and coilgun
A coilgun, also known as a Gauss rifle, is a type of mass driver consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almos ...
s.
Usage
Linear motors are commonly used for actuating high performance industrial automation equipment. Their advantage, unlike any other commonly used actuator, such asball screw
A ball screw (or ballscrew) is a mechanical linear actuator that translates rotational motion to linear motion with little friction. A threaded shaft provides a helical raceway for ball bearings which act as a precision screw. As well as bein ...
, timing belt, or rack and pinion
A rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a circular gear (the '' pinion'') engaging a linear gear (the ''rack''). Together, they convert rotational motion into linear motion. Rotating the pinion causes the rack to be driven ...
, is that they provide any combination of high precision, high velocity, high force and long travel.
Linear motors are widely used. One of the major uses of linear motors is for propelling the shuttle in loom
A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but th ...
s.
Linear motors have been used for sliding doors and various similar actuators. Also, they have been used for baggage handing and even large-scale bulk materials transport.
Linear motors are sometimes used to create rotary motion, for example, they have been used at observatories to deal with the large radius of curvature.
Linear motors may also be used as an alternative to conventional chain-run lift hills for roller coasters. The coaster Maverick
Maverick, Maveric or Maverik may refer to:
History
* Maverick (animal), an unbranded range animal, derived from U.S. cattleman Samuel Maverick
Aviation
* AEA Maverick, an Australian single-seat sportsplane design
* General Aviation Design Burea ...
at Cedar Point uses one such linear motor in place of a chain lift.
A linear motor has been used for accelerating cars for crash test
A crash test is a form of destructive testing usually performed in order to ensure safe design standards in crashworthiness and crash compatibility for various modes of transportation (see automobile safety) or related systems and comp ...
s.
Industrial automation
The combination of high precision, high velocity, high force, and long travel makes brushless linear motors attractive for driving industrial automations equipment. They serve industries and applications such as semiconductorstepper
A stepper is a device used in the manufacture of integrated circuits (ICs) that is similar in operation to a slide projector or a photographic enlarger. ''Stepper'' is short for step-and-repeat camera. Steppers are an essential part of the com ...
s, electronics surface-mount technology
Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referred ...
, automotive cartesian coordinate robot
A Cartesian coordinate robot (also called linear robot) is an industrial robot whose three principal axes of control are linear (i.e. they move in a straight line rather than rotate) and are at right angles to each other. The three sliding joi ...
s, aerospace chemical milling
Chemical milling or industrial etching is the subtractive manufacturing process of using baths of temperature-regulated etching chemicals to remove material to create an object with the desired shape. Other names for chemical etching inclu ...
, optics electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
, healthcare laboratory automation
Laboratory automation is a multi-disciplinary strategy to research, develop, optimize and capitalize on technologies in the laboratory that enable new and improved processes. Laboratory automation professionals are academic, commercial and gover ...
, food and beverage pick and place.
Machine tools
Synchronous linear motoractuator
An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover".
An actuator requires a control device (controlled by control signal) a ...
s, used in machine tools, provide high force, high velocity, high precision and high dynamic stiffness, resulting in high smoothness of motion and low settling time. They may reach velocities of 2 m/s and micron-level accuracies, at short cycle times and a smooth surface finish.
Train propulsion
Conventional rails
All of the following applications are inrapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be c ...
and have the active part of the motor in the cars.
= Bombardier Innovia Metro
= Originally developed in the late 1970s byUTDC
The Urban Transportation Development Corporation Ltd. (UTDC) was a Crown corporation owned by the Government of Ontario, Canada. It was established in the 1970s as a way to enter what was then expected to be a burgeoning market in advanced l ...
in Canada as the Intermediate Capacity Transit System
Innovia Metro is an automated rapid transit system manufactured by Alstom. Innovia Metro systems run on conventional metal rails and pull power from a third rail, but are powered by a linear induction motor that provides traction by pulling on ...
(ICTS). A test track was constructed in Millhaven, Ontario, for extensive testing of prototype cars, after which three lines were constructed:
* Line 3 Scarborough
Line 3 Scarborough (originally known as the Scarborough RT or SRT) is a light rapid transit line that is part of the Toronto subway system in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The line runs entirely within the suburban district of Scarborough, encompas ...
in Toronto (opened 1985)
* Expo Line of the Vancouver SkyTrain
SkyTrain is the medium-capacity rapid transit system in the Metro Vancouver Regional District, serving Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. SkyTrain has of track and uses fully automated trains on grade-separated tracks running on underground ...
(opened 1985 and extended in 1994)
* Detroit People Mover
The Detroit People Mover (DPM) is a elevated automated people mover system in Detroit, Michigan, United States. The system operates in a one-way loop on a single track encircling downtown Detroit, using Intermediate Capacity Transit System lin ...
in Detroit (opened 1987)
ICTS was sold to Bombardier Transportation
Bombardier Transportation was a Canadian-German rolling stock and rail transport manufacturer, headquartered in Berlin, Germany.
It was one of the world's largest companies in the rail vehicle and equipment manufacturing and servicing industry ...
in 1991 and later known as Advanced Rapid Transit (ART) before adopting its current branding in 2011. Since then, several more installations have been made:
* Kelana Jaya Line
The LRT Kelana Jaya Line is a medium-capacity light rapid transit (LRT) line and the first fully automated and driverless rail system in the Klang Valley, Malaysia. It forms a part of the Klang Valley Integrated Transit System in and around ...
in Kuala Lumpur (opened 1998 and extended in 2016)
* Millennium Line
The Millennium Line is the second line of the SkyTrain rapid transit system in the Metro Vancouver region of British Columbia, Canada. The line is owned and operated by BC Rapid Transit Company, a subsidiary of TransLink, and links the cities ...
of the Vancouver SkyTrain (opened 2002 and extended in 2016)
* AirTrain JFK
AirTrain JFK is an elevated people mover system and airport rail link serving John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK Airport) in New York City. The driverless system operates 24/7 and consists of three lines and nine stations within the ...
in New York (opened 2003)
* Airport Express (Beijing Subway)
The Capital Airport Express of the Beijing Subway (), also known by the initials ABC, Airport Beijing City, is an airport rail link from Beixingqiao station to the Beijing Capital International Airport. The line became operational on July 1 ...
(opened 2008)
* Everline
EverLine is a fully automated driverless people mover line in Yongin, Seoul Capital Area connecting Everland, South Korea's most popular theme park, to Bundang Line of the Seoul Metropolitan Subway. The system is identical to AirTrain JFK people ...
in Yongin, South Korea (opened 2013)
All Innovia Metro systems use third rail
A third rail, also known as a live rail, electric rail or conductor rail, is a method of providing electric power to a railway locomotive or train, through a semi-continuous rigid conductor placed alongside or between the rails of a railway t ...
electrification.
= Japanese Linear Metro
= One of the biggest challenges faced by Japanese railway engineers in the 1970s to the 1980s was the ever increasing construction costs of subways. In response, the Japan Subway Association began studying on the feasibility of the "mini-metro" for meeting urban traffic demand in 1979. In 1981, the Japan Railway Engineering Association studied on the use oflinear induction motors
A linear induction motor (LIM) is an alternating current (AC), asynchronous linear motor that works by the same general principles as other induction motors but is typically designed to directly produce motion in a straight line. Characteristica ...
for such small-profile subways and by 1984 was investigating on the practical applications of linear motors for urban rail with the Japanese Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism
The , abbreviated MLIT, is a ministry of the Japanese government.国土交通省設置法 ...
. In 1988, a successful demonstration was made with the Limtrain at Saitama and influenced the eventual adoption of the linear motor for the Nagahori Tsurumi-ryokuchi Line in Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of 2. ...
and Toei Line 12 (present-day Toei Oedo Line Toei or Tōei may refer to:
* Tōei, Aichi, Japan
* Toei Company, Japanese film and television production company
** Toei Animation, their animation subsidiary
* , Japanese abbreviation meaning "operated by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government"
**Tran ...
) in Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 ...
.
To date, the following subway lines in Japan use linear motors and use overhead line
An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit electrical energy to electric locomotives, trolleybuses or trams. It is known variously as:
* Overhead catenary
* Overhead contact system (OCS)
* Overhead equipmen ...
s for power collection:
*Two Osaka Metro
The is a major rapid transit system in the Osaka Metropolitan Area of Japan, operated by the Osaka Metro Company, Ltd. It serves the city of Osaka and the adjacent municipalities of Higashiosaka, Kadoma, Moriguchi, Sakai, Suita, and Yao. O ...
lines in Osaka:
** Nagahori Tsurumi-ryokuchi Line (opened 1990)
**Imazatosuji Line
The is a rapid transit line of Osaka Metro, running from Itakano Station in Higashiyodogawa-ku to Imazato Station in Higashinari-ku, all within Osaka city. Its official name is , and in MLIT publications, it is written as . Station number ...
(opened 2006)
*Toei Ōedo Line
The is a subway line in Tokyo, Japan, operated by the Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation (Toei). It commenced full operations on December 12, 2000; using the Japanese calendar this reads "12/12/12" as the year 2000 equals Heisei 12. T ...
in Tokyo (opened 2000)
*Kaigan Line
The , also known as the "Yumekamome" ( ja, 夢かもめ), is one of two lines of the Kobe Municipal Subway. Trains of the line are propelled by linear motors. This is the third linear motor rapid transit line to be built in Japan.
History
C ...
of the Kobe Municipal Subway
The is a rapid transit system in Kobe, Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan. Like other large Japanese cities, Kobe's subway system is heavily complemented by suburban rail. In addition, two people mover lines also serve the Kobe area: the Port Island Line ...
(opened 2001)
*Nanakuma Line
The is a subway line, part of the Fukuoka City Subway system in Fukuoka, Japan. It runs from Hashimoto Station in Nishi Ward to Tenjin-Minami Station in Chūō Ward, all within Fukuoka. The line's color on maps is green. Officially, the line ...
of the Fukuoka City Subway
The serves Fukuoka, Japan. It consists of three subway lines, the Kūkō, or Airport Line, the Hakozaki Line and the Nanakuma Line).
The lines are operated by the Fukuoka City Transportation Bureau. Unlike most other public operators in Japa ...
(opened 2005)
*Yokohama Municipal Subway Green Line
The is a rapid transit line serving Yokohama in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. It is the shorter of the two lines in the Yokohama Municipal Subway system operated by Yokohama City Transportation Bureau. Its formal designation is Line 4, and it is ...
(opened 2008)
*Sendai Subway Tōzai Line
The is one of the two lines of the Sendai Subway system operated by the Sendai City Transportation Bureau in the city of Sendai, Japan. It opened on 6 December 2015. The Tozai Line uses linear motor propulsion.
Stations
From the start of op ...
(opened 2015)
In addition, Kawasaki Heavy Industries
(or simply Kawasaki) is a Japanese Public company, public multinational corporation manufacturer of motorcycles, engines, Heavy equipment (construction), heavy equipment, aerospace and Military, defense equipment, rolling stock and ships, headq ...
has also exported the Linear Metro to the Guangzhou Metro
The Guangzhou Metro () ( and ) is the rapid transit system of the city of Guangzhou in Guangdong Province of China. It is operated by the state-owned Guangzhou Metro Corporation and was the fourth metro system to be built in mainland China, af ...
in China; all of the Linear Metro lines in Guangzhou use third rail electrification:
* Line 4 (opened 2005)
* Line 5 (opened 2009).
* Line 6 (opened 2013)
Monorail
* There is at least one known monorail system which is not magnetically levitated, but nonetheless uses linear motors. This is the Moscow Monorail. Originally, traditional motors and wheels were to be used. However, it was discovered during test runs that the proposed motors and wheels would fail to provide adequate traction under some conditions, for example, when ice appeared on the rail. Hence, wheels are still used, but the trains use linear motors to accelerate and slow down. This is possibly the only use of such a combination, due to the lack of such requirements for other train systems. * TheTELMAGV
The TELMAG (''Tren Electromagnético'' - Spanish for 'Electromagnetic Train') is an ongoing research project which was born in the Instituto Venezolano de Investigaciones Científicas ( IVIC) in 1967, and later continued by the Universidad de Los ...
is a prototype of a monorail system that is also not magnetically levitated but uses linear motors.
Magnetic levitation
 * High-speed trains:
**
* High-speed trains:
** Transrapid
Transrapid is a German-developed high-speed monorail train using magnetic levitation. Planning for the Transrapid system started in 1969 with a test facility for the system in Emsland, Germany completed in 1987. In 1991, technical readi ...
: first commercial use in Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flow ...
(opened in 2004)
** SCMaglev
The SCMaglev (superconducting maglev, formerly called the MLU) is a magnetic levitation (maglev) railway system developed by Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central) and the Railway Technical Research Institute.
On 21 April 2015, a manned sev ...
, under construction in Japan (fastest train in the world, planned to open by 2027)
* Rapid transit:
** Birmingham Airport, UK (opened 1984, closed 1995)
** M-Bahn
The M-Bahn or Magnetbahn was an elevated Maglev train line operating in Berlin, Germany, experimentally from 1984 and in passenger operation from 1989 to 1991. The line was in length, and featured three stations, two of which were newly construc ...
in Berlin, Germany (opened in 1989, closed in 1991)
** Daejeon EXPO, Korea (ran only 1993)
** HSST: Linimo line in Aichi Prefecture, Japan (opened 2005)
** Incheon Airport Maglev
The Incheon Airport Maglev is a maglev line in South Korea opened on 3 February 2016. It is the world's second commercially operating unmanned urban maglev line after Japan's Linimo. The trains are lighter, cutting construction costs in half ...
(opened July 2014)
** Changsha Maglev Express
The Changsha Maglev Express () is a medium-low speed magnetic levitation, or ''maglev'' line in Changsha, China. This is China's second maglev line, after Shanghai Maglev, and the first domestically built maglev line that uses indigenous techno ...
(opened 2016)
** S1 line of Beijing Subway
The Beijing Subway is the rapid transit system of Beijing Municipality that consists of 25 lines including 20 rapid transit lines, two airport rail links, one maglev line and 2 light rail lines, and 463 stations. The rail network extends acro ...
(opened 2017)
Amusement rides
There are many roller coasters throughout the world that use LIMs to accelerate the ride vehicles. The first being ''Flight of Fear
Flight of Fear is the name of two identical enclosed roller coasters located at Kings Island and Kings Dominion amusement parks. Built and designed by Premier Rides, they were the world's first launched roller coasters to feature linear inducti ...
'' at Kings Island
Kings Island is a amusement park located northeast of Cincinnati in Mason, Ohio, United States. Owned and operated by Cedar Fair, the park first opened in 1972 by the Taft Broadcasting Company. It was part of a larger effort to move and expan ...
and Kings Dominion
Kings Dominion is an amusement park located in Doswell, Virginia, north of Richmond and south of Washington, D.C. Owned and operated by Cedar Fair, the park opened to the public on May 3, 1975, and features more than 60 rides, shows and att ...
, both opening in 1996. Battlestar Galctica: Human VS Cylon & Revenge of the Mummy
Revenge of the Mummy, officially named Revenge of the Mummy: The Ride, is an enclosed roller coaster located at Universal Studios Florida, Universal Studios Hollywood, and Universal Studios Singapore. Its theme is based on ''The Mummy'' film f ...
at Universal Studios Singapore
Universal Studios Singapore (abbreviation: USS) is a theme park located within the Resorts World Sentosa at Sentosa, Singapore. It features 28 Theme park#Rides and attractions, rides, shows, and Theme park#Rides and attractions, attractions in ...
opened in 2010. They both use LIMs to accelerate from certain point in the rides.
Revenge of the Mummy also is located at Universal Studios Hollywood
Universal Studios Hollywood is a film studio and theme park
An amusement park is a park that features various attractions, such as rides and games, as well as other events for entertainment purposes. A theme park is a type of amusemen ...
and Universal Studios Florida
Universal Studios Florida (also known as Universal Studios or USF) is a theme park located in Orlando, Florida. Primarily themed to movies, television and other aspects of the entertainment industry, the park opened to the public on June 7, 1990 ...
. The Incredible Hulk Coaster and VelociCoaster
VelociCoaster (marketed as Jurassic World VelociCoaster) is a launched roller coaster at Universal's Islands of Adventure in Orlando, Florida. Manufactured by Intamin and themed to the Velociraptors from the '' Jurassic World'' film franchis ...
at Universal's Islands of Adventure
Universal's Islands of Adventure (also known as Islands of Adventure or IOA), originally called Universal Studios Islands of Adventure, is a theme park located in Orlando, Florida
Orlando () is a city in the U.S. state of Florida and is th ...
also uses linear motors. At Walt Disney World
The Walt Disney World Resort, also called Walt Disney World or Disney World, is an entertainment resort complex in Bay Lake and Lake Buena Vista, Florida, United States, near the cities of Orlando and Kissimmee. Opened on October 1, 1971, th ...
, Rock 'n' Roller Coaster Starring Aerosmith
Rock 'n' Roller Coaster Starring Aerosmith is an enclosed, launched roller coaster located at Disney's Hollywood Studios within Walt Disney World. Manufactured by Vekoma, the roller coaster opened to the public on July 29, 1999. It uses linear ...
at Disney's Hollywood Studios
Disney's Hollywood Studios is a theme park at the Walt Disney World Resort in Bay Lake, Florida, near Orlando. It is owned and operated by The Walt Disney Company through its Parks, Experiences and Products division. Based on a concept by Ma ...
and ''Guardians of the Galaxy'': Cosmic Rewind at Epcot
Epcot, stylized in all uppercase as EPCOT, is a theme park at the Walt Disney World Resort in Bay Lake, Florida. It is owned and operated by The Walt Disney Company through its Parks, Experiences and Products division. Inspired by an unreal ...
both use LSM to launch their ride vehicles into their indoor ride enclosures.
Aircraft launching
*Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System
The Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS) is a type of aircraft launching system developed by General Atomics for the United States Navy. The system launches carrier-based aircraft by means of a catapult employing a linear induction ...
Proposed and research
*Launch loop
A launch loop, or Lofstrom loop, is a proposed system for launching objects into orbit using a moving cable-like system situated inside a sheath attached to the Earth at two ends and suspended above the atmosphere in the middle. The design conce ...
– A proposed system for launching vehicles into space using a linear motor powered loop
* StarTram
StarTram is a proposed space launch system propelled by maglev. The initial Generation 1 facility would launch cargo only, launching from a mountain peak at an altitude of with an evacuated tube staying at local surface level; it has been clai ...
– Concept for a linear motor on extreme scale
* Tether cable catapult system
* Aérotrain S44 – A suburban commuter hovertrain
A hovertrain is a type of high-speed train that replaces conventional steel wheels with hovercraft lift pads, and the conventional railway bed with a paved road-like surface, known as the ''track'' or ''guideway''. The concept aims to eliminat ...
prototype
* Research Test Vehicle 31 – A hovercraft-type vehicle guided by a track
* Hyperloop
A hyperloop is a proposed high-speed transportion system for both public and goods transport. The idea was picked up by Elon Musk to describe a modern project based on the vactrain concept (first appearance in 1799). Hyperloop systems compris ...
– a conceptual high-speed transportation system put forward by entrepreneur Elon Musk
* Elevator
An elevator or lift is a wire rope, cable-assisted, hydraulic cylinder-assisted, or roller-track assisted machine that vertically transports people or freight between floors, levels, or deck (building), decks of a building, watercraft, ...
* Lift
Lift or LIFT may refer to:
Physical devices
* Elevator, or lift, a device used for raising and lowering people or goods
** Paternoster lift, a type of lift using a continuous chain of cars which do not stop
** Patient lift, or Hoyer lift, mobil ...
* Magway - a UK freight delivery system under research and development that aims to deliver goods in pods via 90 cm diameter pipework under and over ground.
See also
*Linear actuator
A linear actuator is an actuator that creates motion in a straight line, in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. Linear actuators are used in machine tools and industrial machinery, in computer Peripheral, periphera ...
* Linear induction motor
A linear induction motor (LIM) is an alternating current (AC), asynchronous linear motor that works by the same general principles as other induction motors but is typically designed to directly produce motion in a straight line. Characteristic ...
* Linear motion
Linear motion, also called rectilinear motion, is one-dimensional motion along a straight line, and can therefore be described mathematically using only one spatial dimension. The linear motion can be of two types: uniform linear motion, with co ...
* Maglev
Maglev (derived from '' magnetic levitation''), is a system of train transportation that uses two sets of electromagnets: one set to repel and push the train up off the track, and another set to move the elevated train ahead, taking advantage ...
* Online Electric Vehicle
* Reciprocating electric motor
A reciprocating electric motor is a motor in which the armature moves back and forth rather than circularly. Early electric motors were sometimes of the reciprocating type, such as those made by Daniel Davis in the 1840s. Today, reciprocating elect ...
* Sawyer motor
* Tubular linear motor A tubular linear motor is a type of linear electric motor with a forcer consisting of a series of solenoids wrapped around a cylinder enclosing a movable rod that contains a number of strong cylindrical permanent magnets aligned in alternating and ...
References
External links
Design equations, spreadsheet, and drawings
Motor torque calculation
{{DEFAULTSORT:Linear Motor Electric motors English inventions Linear motion